Every year millions of tourists, art connoisseurs and heritage enthusiasts visit Ajanta, the mural capital of India located in Sahyadri Hills of Maharashtra. The mural heritage of Ajanta was however short-lived, thanks to the fall of Vakatakas and their patronage.
The features that were laid in Ajanta was however found in full bloom in the Pallava Court at Kanchipuram, 1000 km away from the Vakataka capital. Unfortunately very little of Pallava murals have survived today. Following the Pallavas, it was the Vijayanagar and then Nayaka rulers who also made Kanchi as a canvas for their mural sojourn.
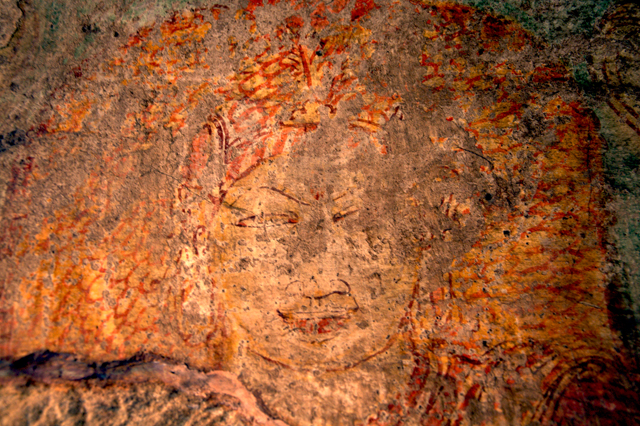

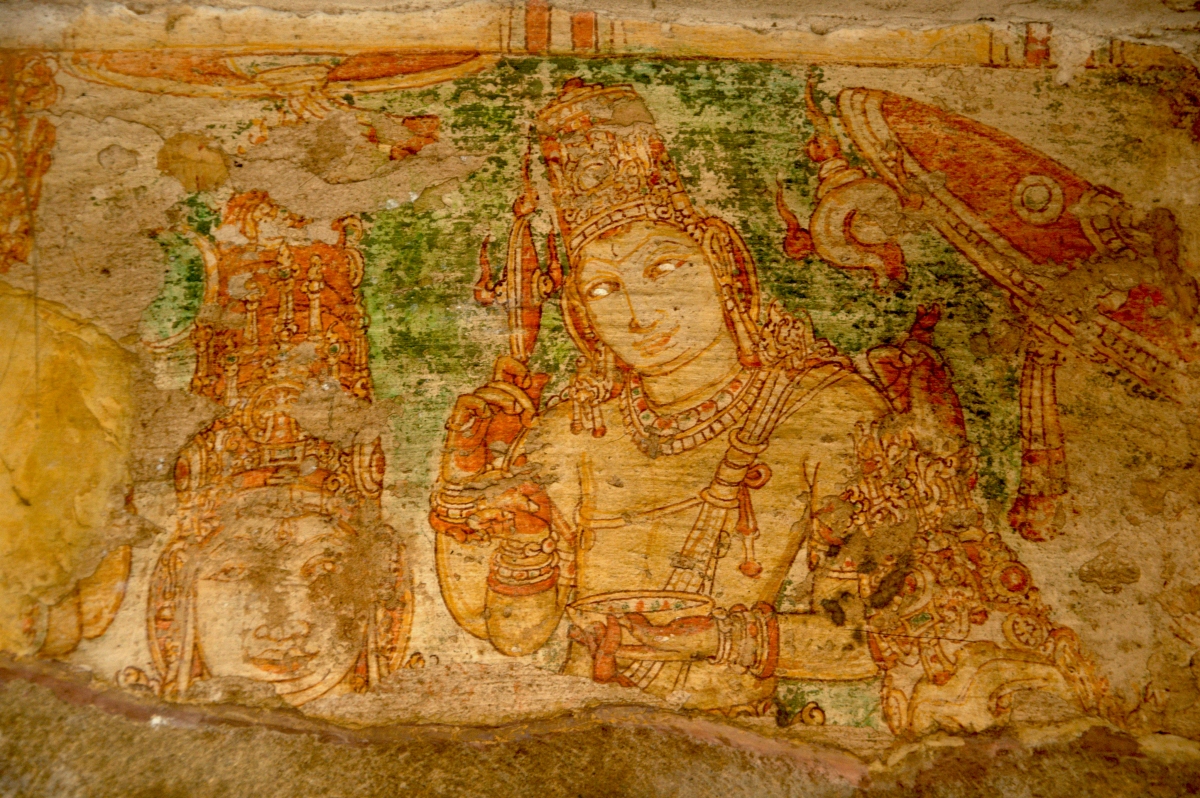
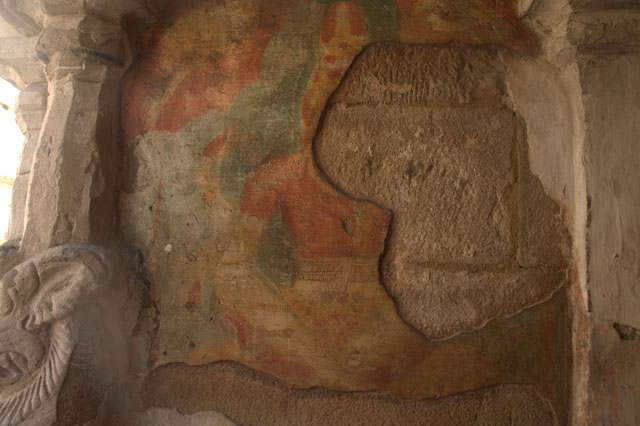
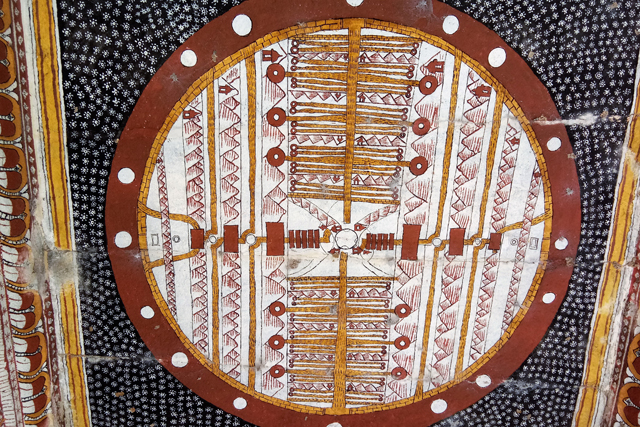
Pallava – Image Courtesy: Vijay Sundararaman Iyer

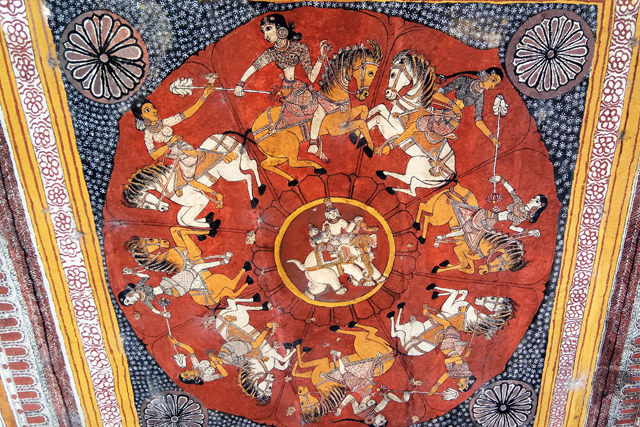
Vijayanagar – Image Courtesy: Vijay Sundararaman Iyer
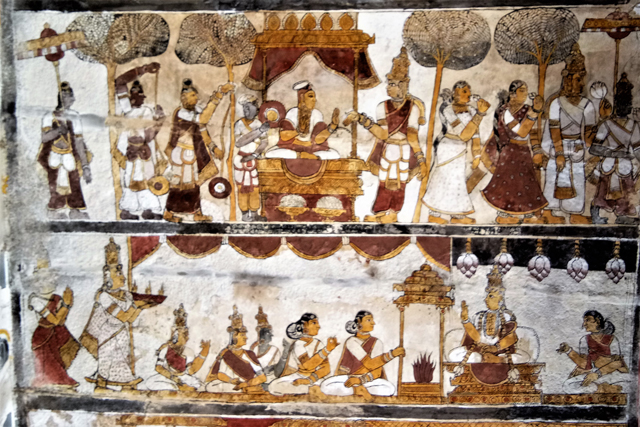

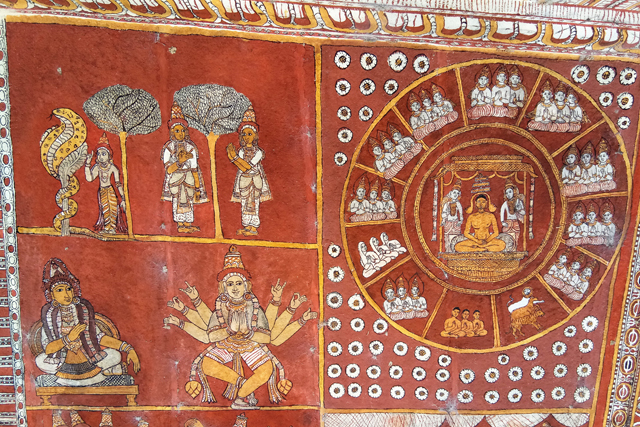
Nayaka
Pallavas who made Kanchipuram as their capital were great patrons of art. Mahendra Verman I, the founder of the dynasty was credited for the introduction of rock-cut architecture in Tamil Nadu in 7th Century CE. Because of his artistic talent, he was titled variously as Vichitra Chitta, Mattavilasa, Chaitrahari or Chitrakarapuli. However, none of Mahendra’s murals has survived at Kanchi today. What has remained are from the period of Rajasimha, who ruled towards the end of the 7th century CE.
Also, Read here:
Ajanta – India’s First Renaissance
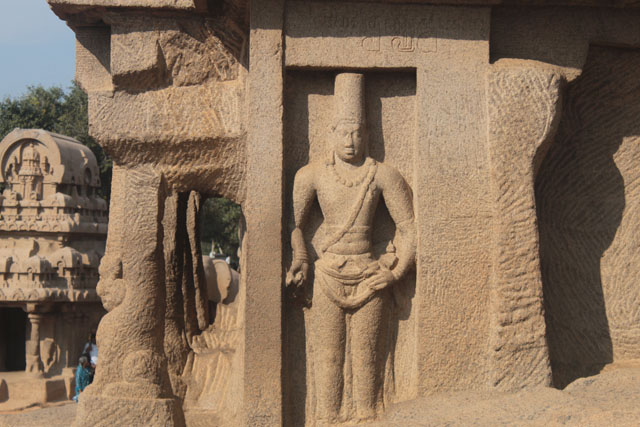

Mahendra Verman I at Mahabalipuram
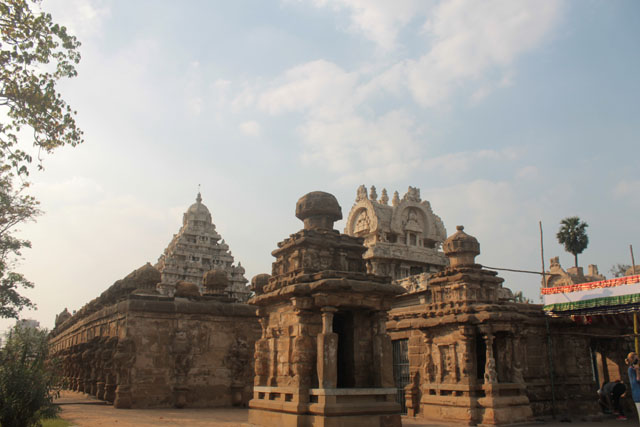

Kailashnath Temple Kanchipuram
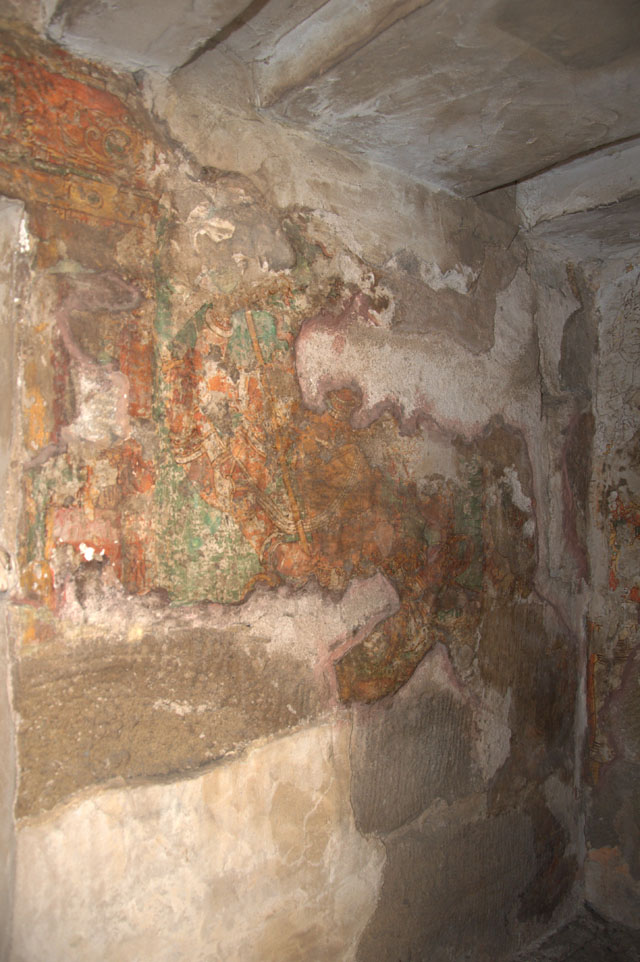
Rajasimha’s murals have also mostly gone; however, a close observation helps us to find traces of lines and colours on small cells in the pradakshina path.
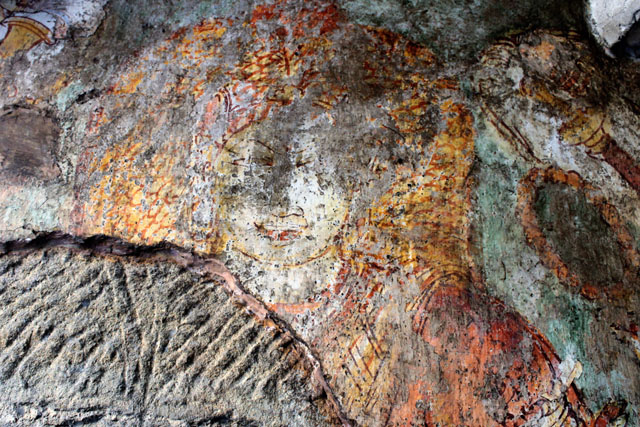
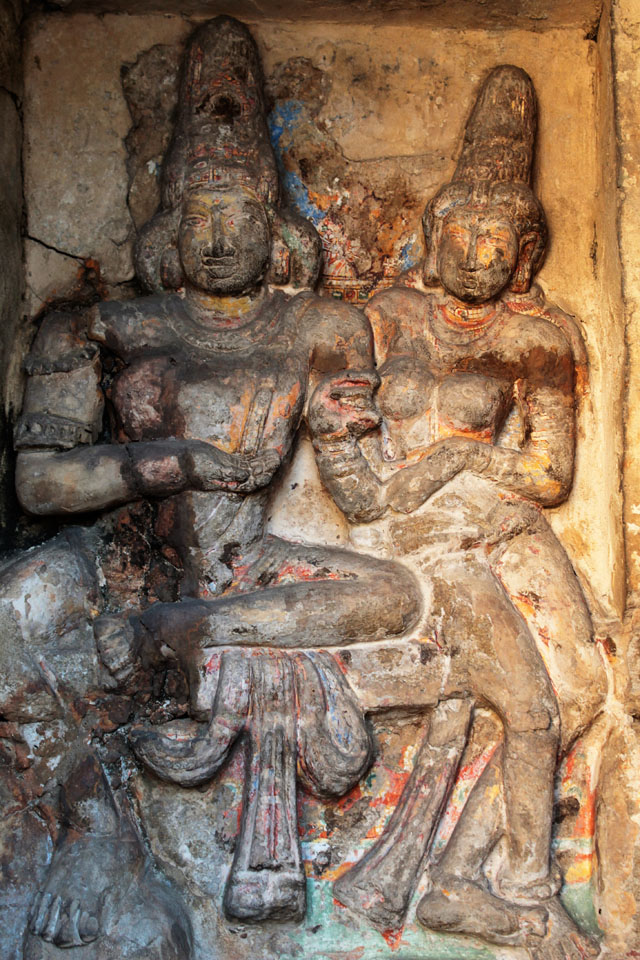
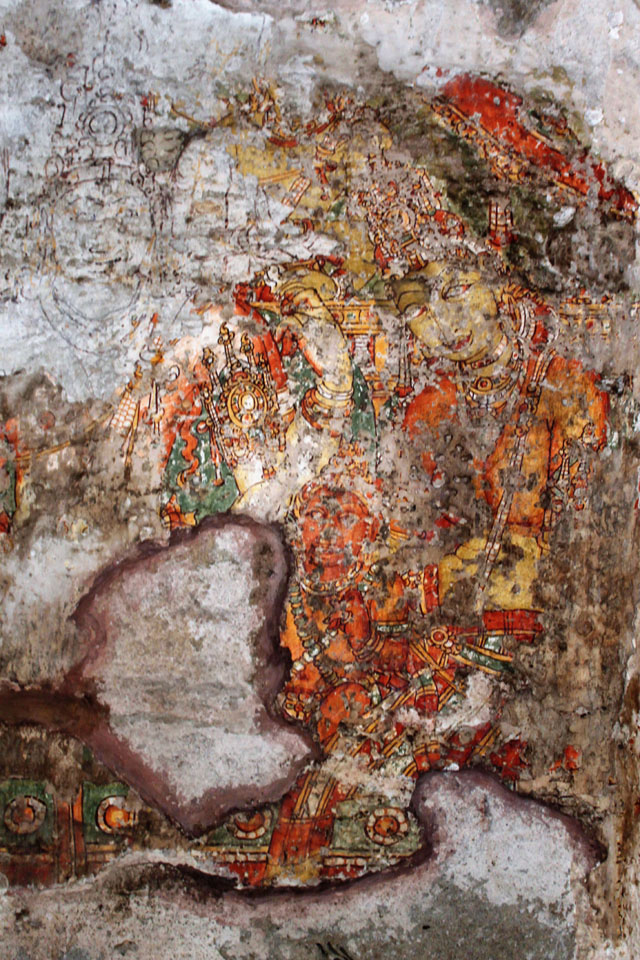
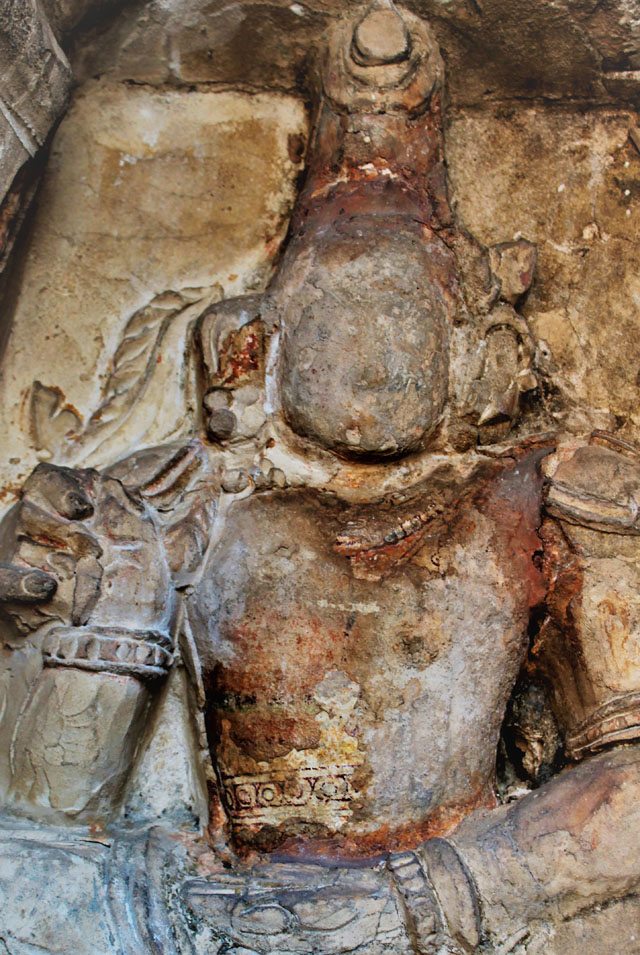
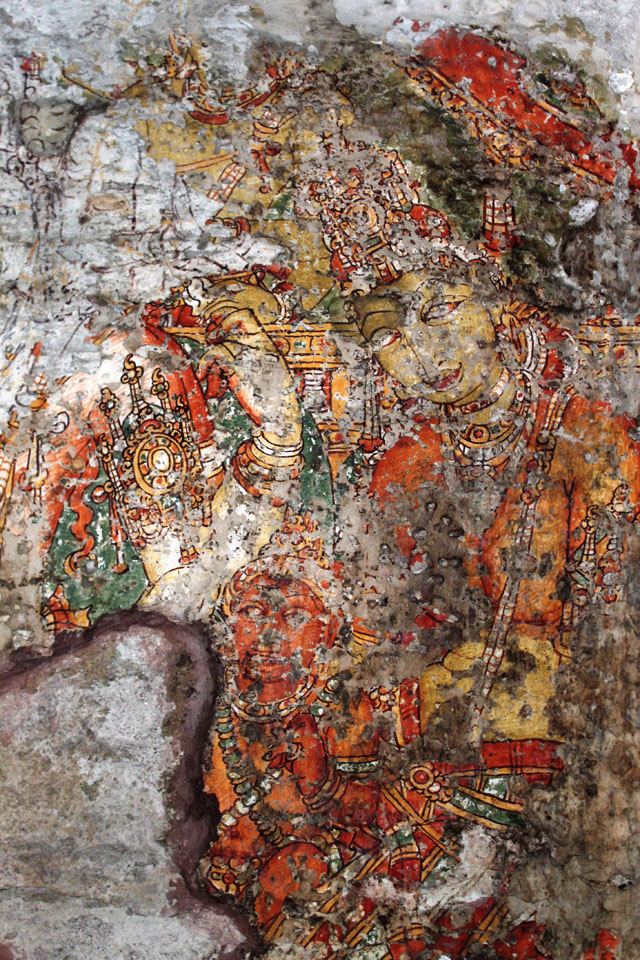
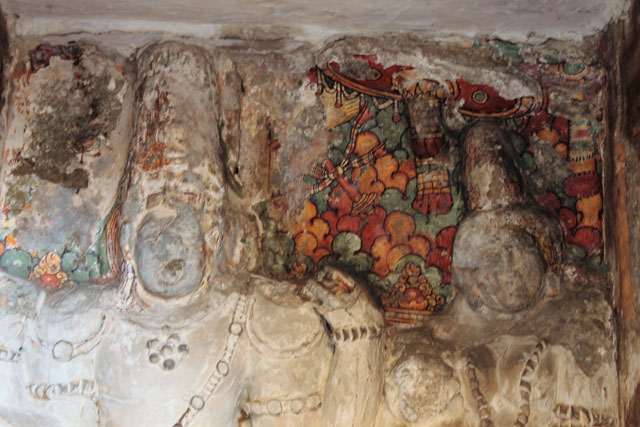
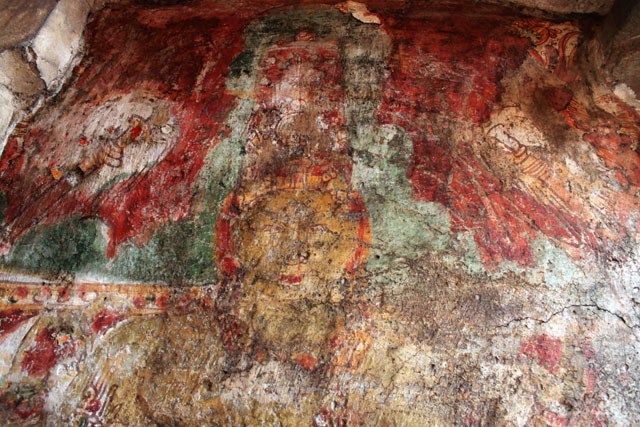
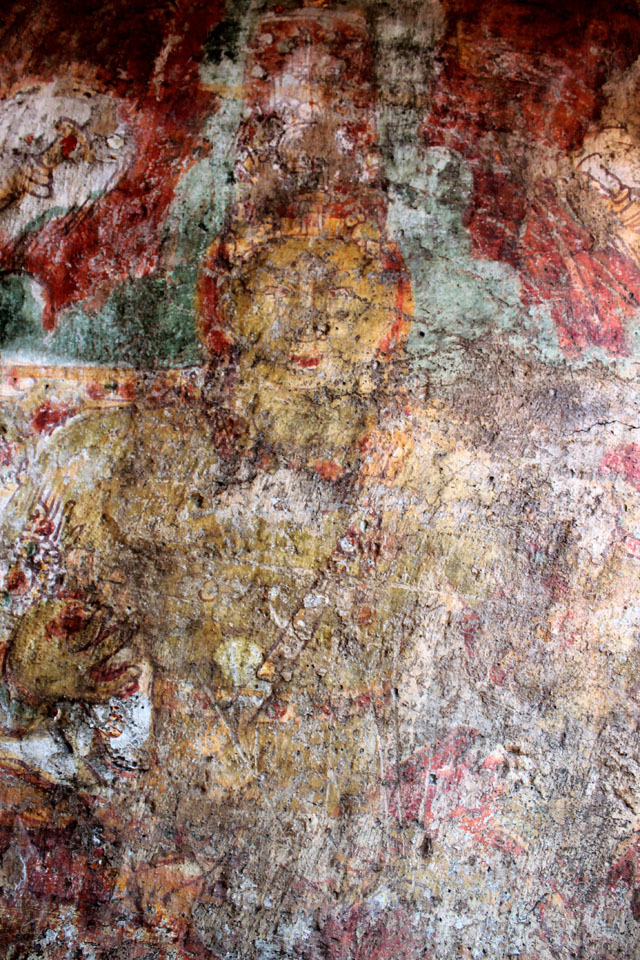
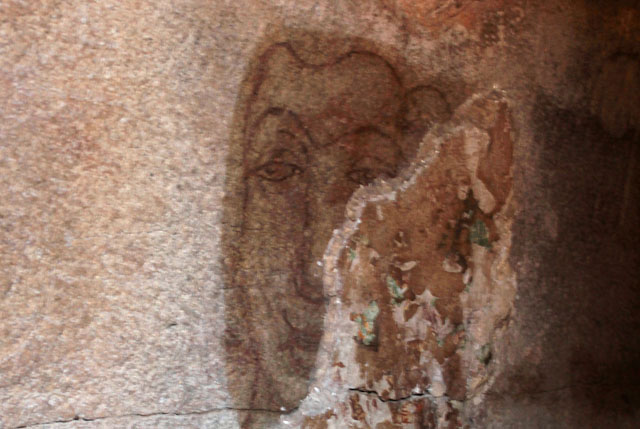
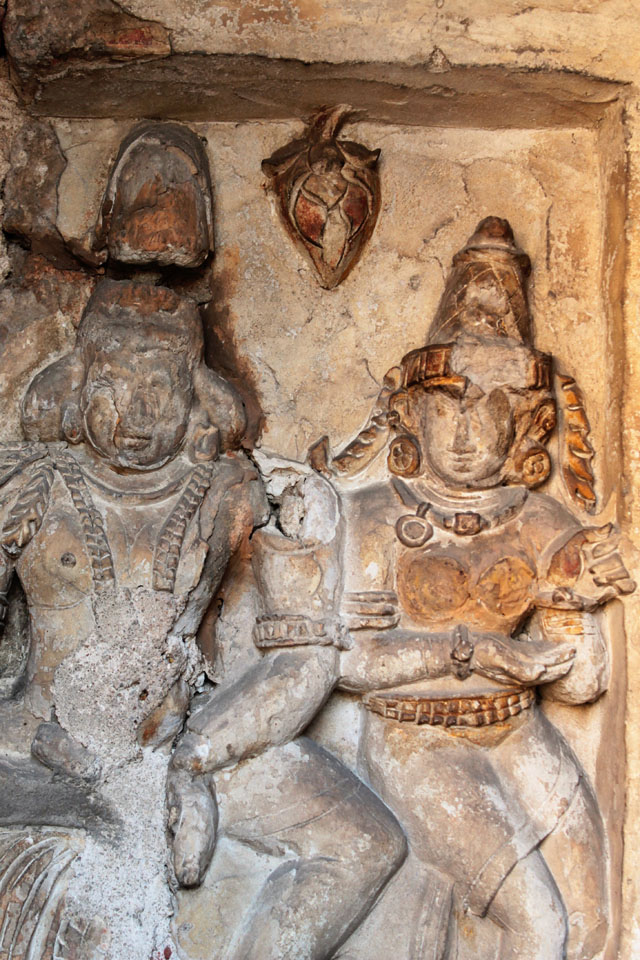
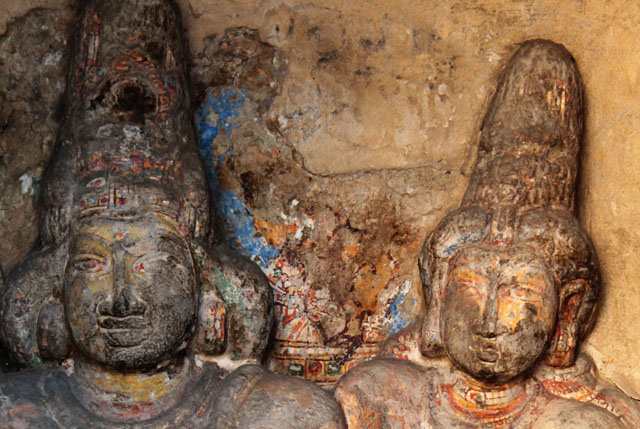
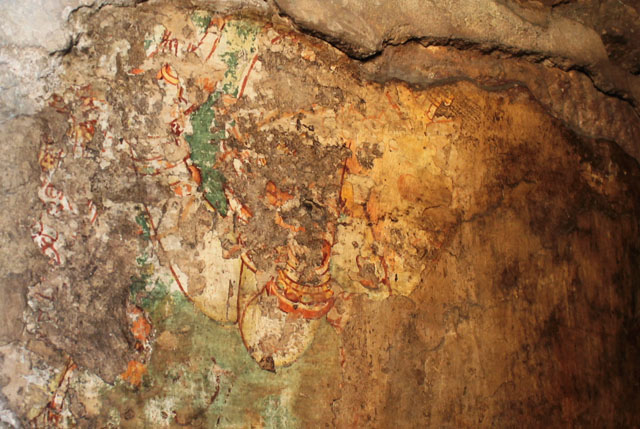
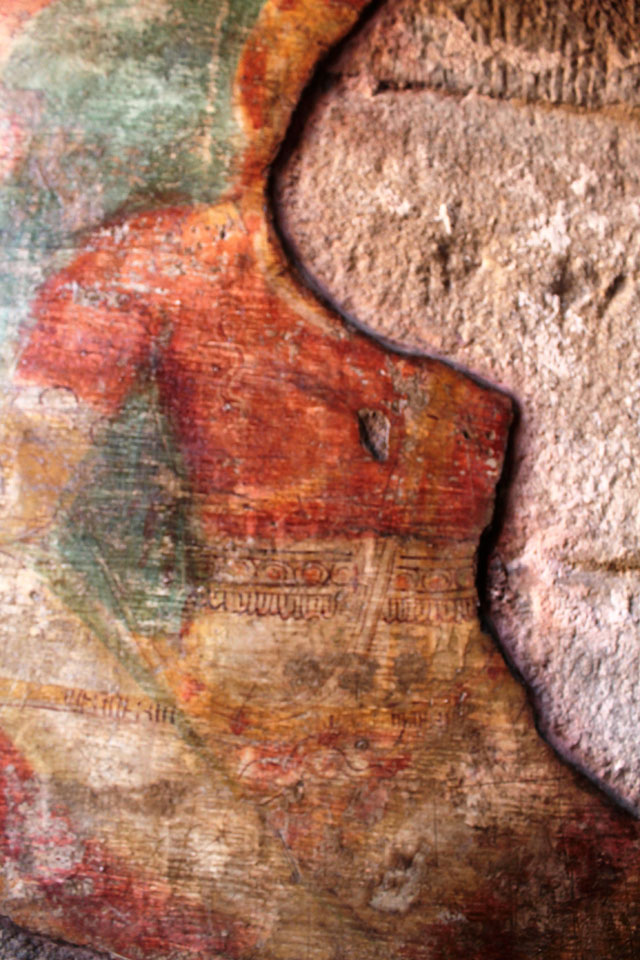
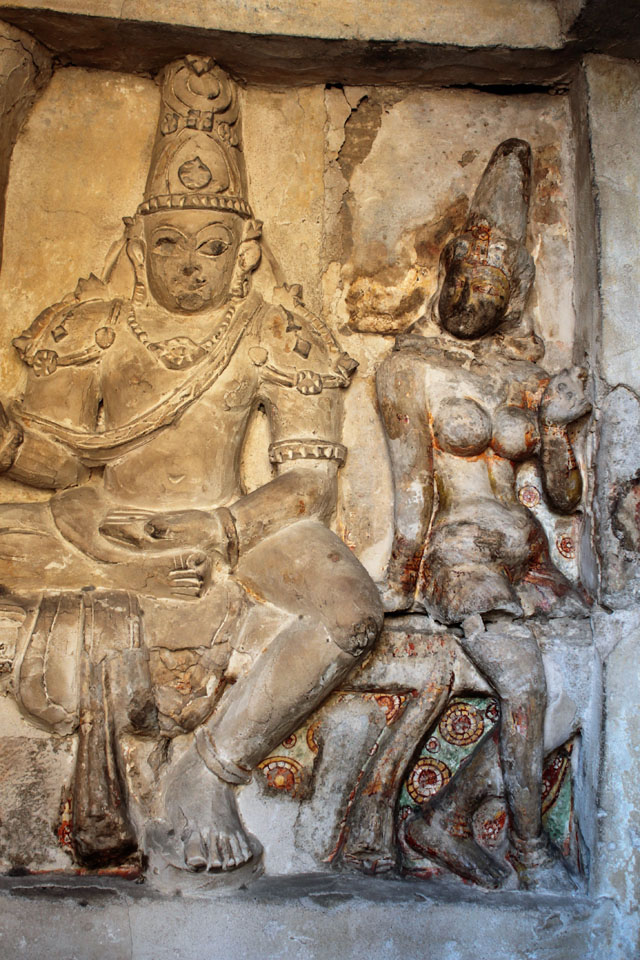
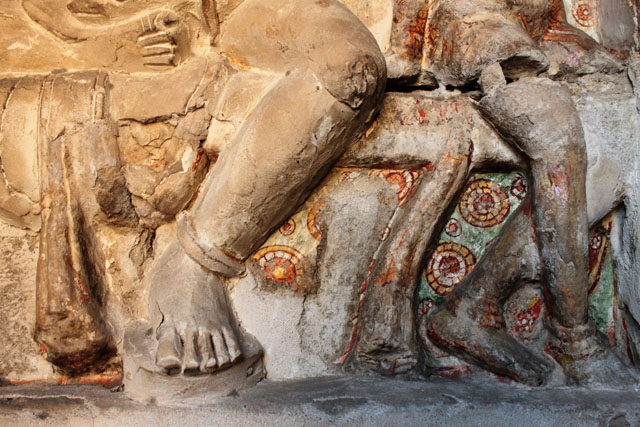

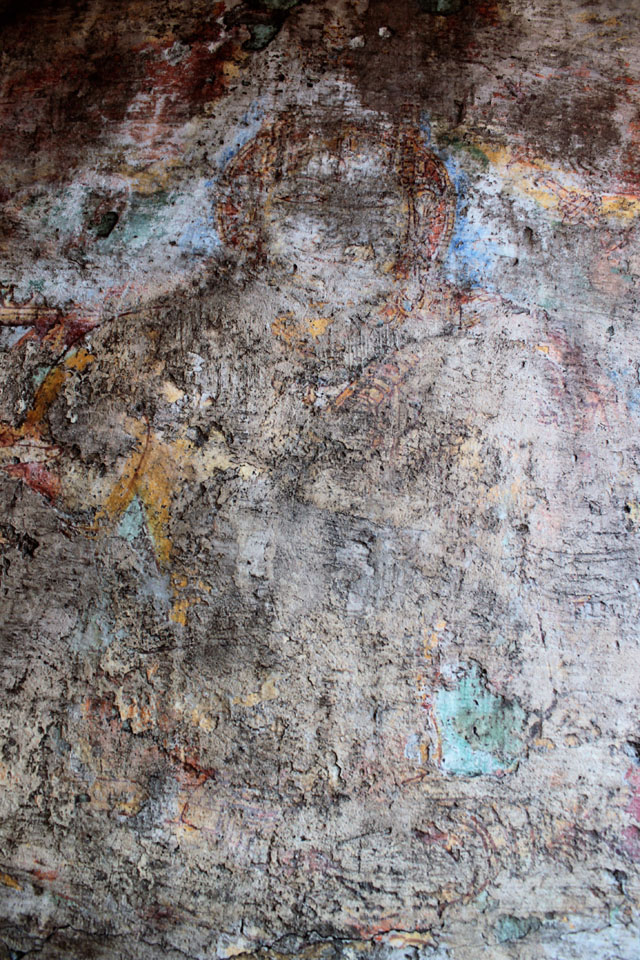









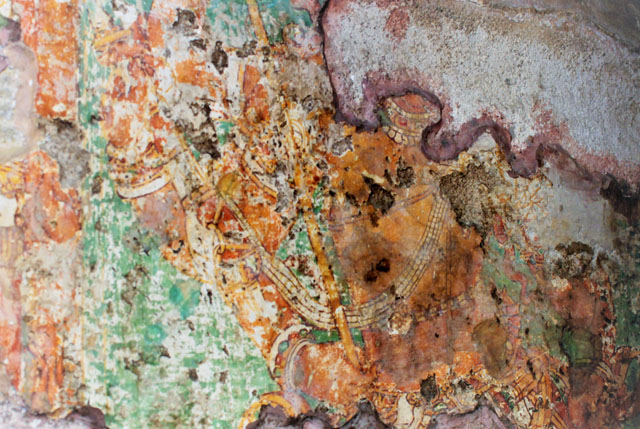








In cell 9 there are remains of fragments of upper and lower arms of Shiva and in cell 11, one finds the beautiful face of Shiva depicted in Pallava style with only a part of the nose, cheek, kandala and yognopavita. In cell 23, there are remnants of a painting of Shiva and cell no 34 there remain traces of a mahapurusha (kirata, shoulder and thigh are left). However, the most striking remains are that of a Samakanda mural in red on the back wall of cell 41. The colours are gone, but the line of composition of the seated Shiva and Parvati and a lovely attendant of Parvati are an indication of the excellence of the artist’s ability. Depicting Samakanda was a favourite Pallava theme for murals as well as sculptures. The curve of the arms and legs, the excellent proportion of the limbs, details such as tussle, the folds of the garments and the ornamentation are surpassed only by the very adorable baby Skanda. Parvati’s figure is full of feminine grace.
Kanchipuram is located at a distance of 72 km from Chennai off Bangalore Highway. The city is also well connected by rail. Located on the banks of Vegavathi River, Kanchipuram has a rich history and heritage. It was the administrative capital of Pallavas in the 7th century. It was later ruled by Cholas and Vijayanagar rulers. Kanchipuram was a great centre of education in historical time. Of the 108 holy temples, the best -known are Varadharaja Perumal Temple, Ekambareswarar Temple, Kamakshi Amman Temple, and Kumarakottam Temple. The city is well-known for its hand-woven saree industry known as Kanchipuram Silk. While at Ekambaeswarar Temple relish Kanchipuram Idli which is offered to temple as prasadam every morning.
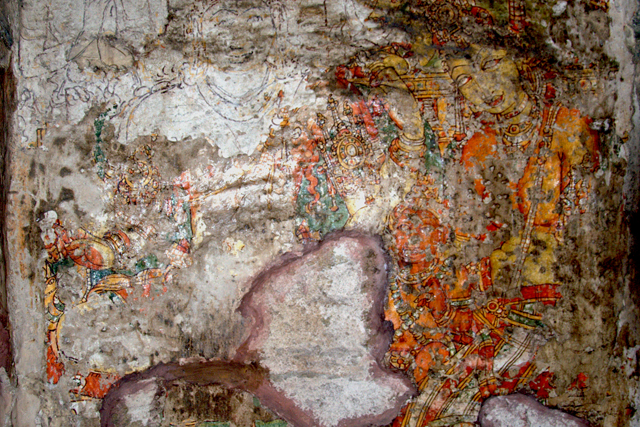
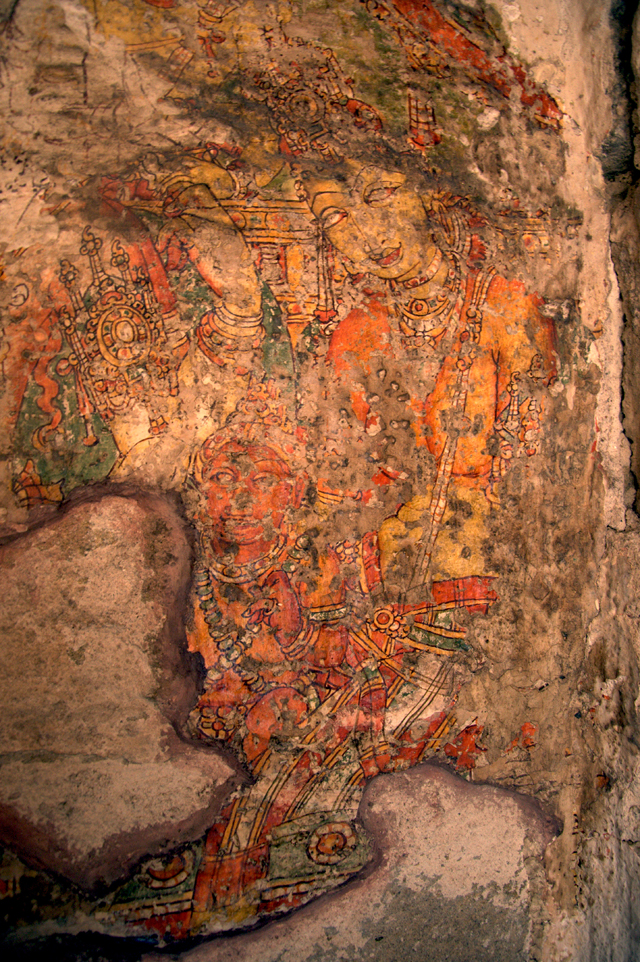
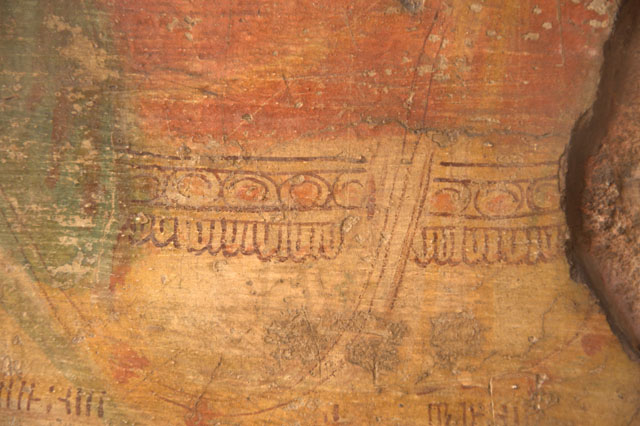





Images Courtesy: Vijay Sundararaman Iyer
One other painting which is in a fair state of preservation is that of Kinnara and Kinnari, a half human and a half bird couple who are celestial musicians.
The tradition of Pallava murals had carried forward the Ajanta tradition. They display the same grace of line and movement. The artists were masters of brushwork and figure drawings. The paintings were executed on a smoothly prepared surface in the fresco style. The colours used are black, red, white, yell, blue and green.
The Pallava murals of Kanchipuram are known for their fully open and wide eyes in accordance with South Indian ideals which demands wide, beautiful eyes as they are most striking features in the face. Faces are round and fuller.
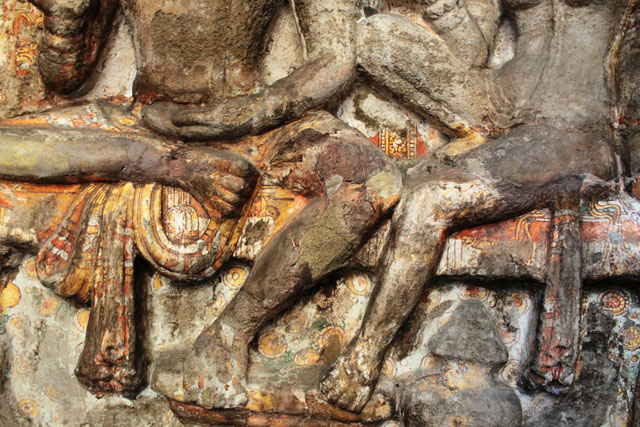
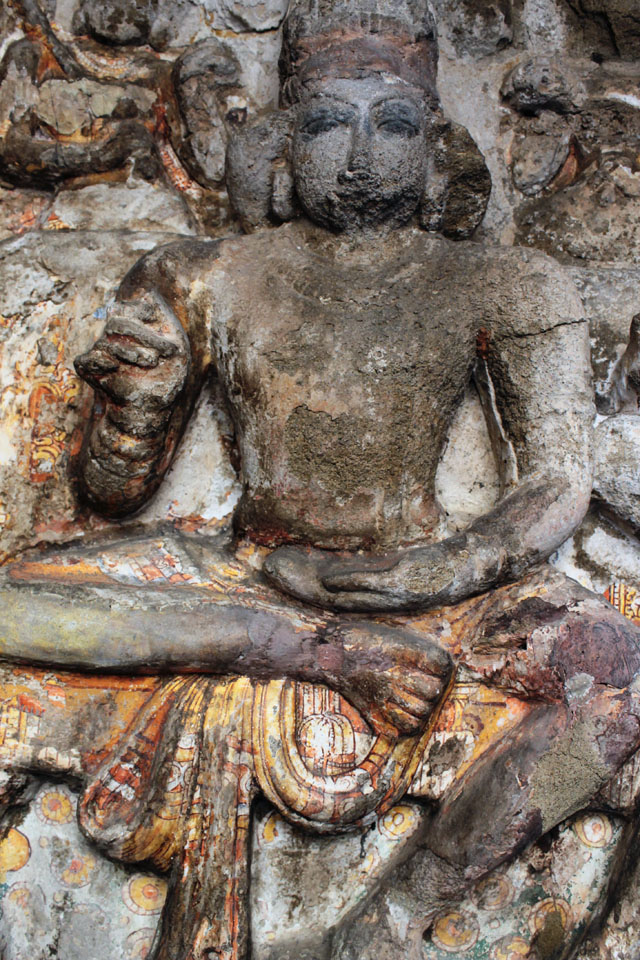
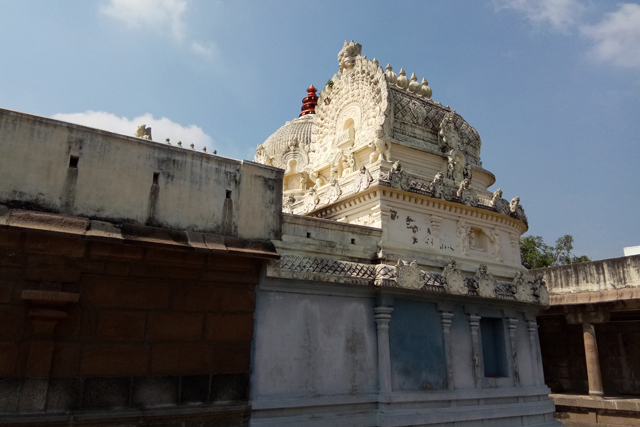
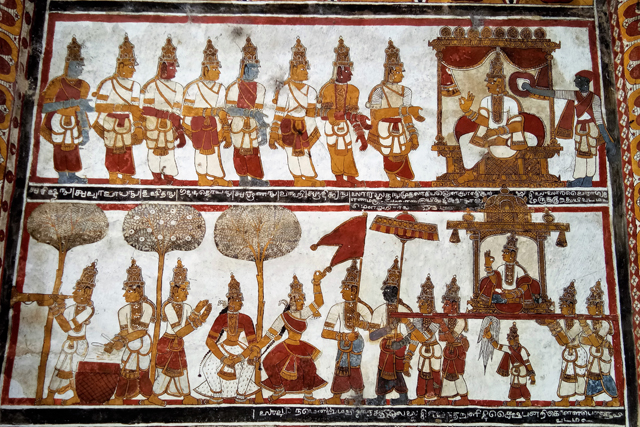
The Pallava tradition of murals was revived much later in the 16th century during the Vijayanagar Period at the time of Achyutadevaraya who had commissioned murals on the walls and ceilings of Vardarajaperumal temple at Kanchipuram.
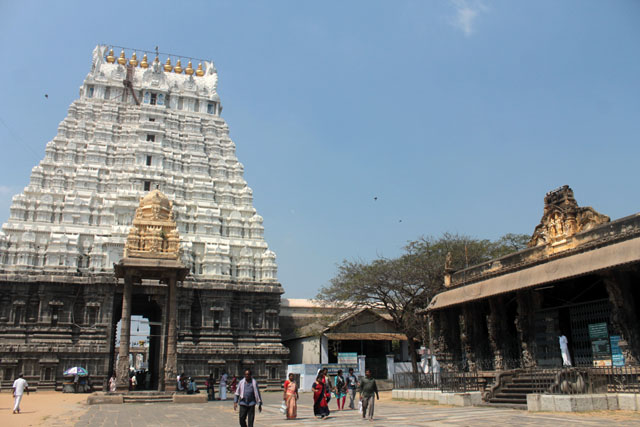

Vardarajaperumal Temple
In Andal Unjal Mandapa, the ceiling is carved with stories of Krishna from the Bhagavata Purana and Harivamsa, stories of Kaliyamardana, Vishnu with his consorts and so on.
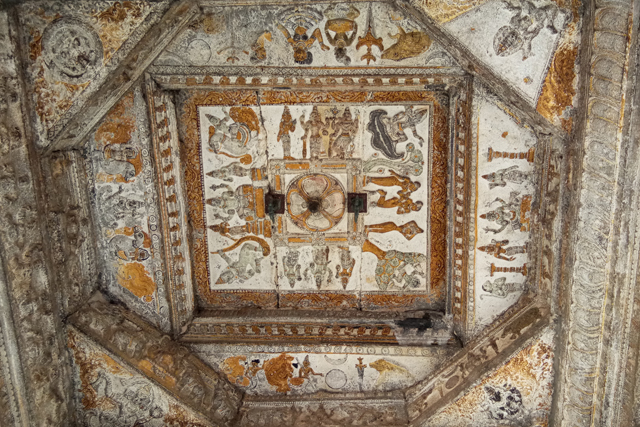
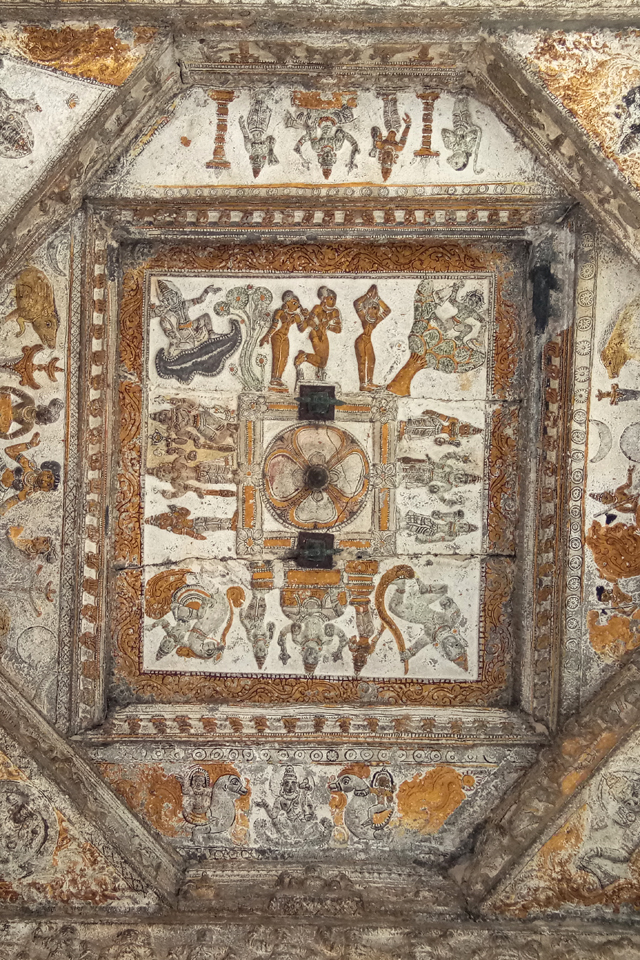
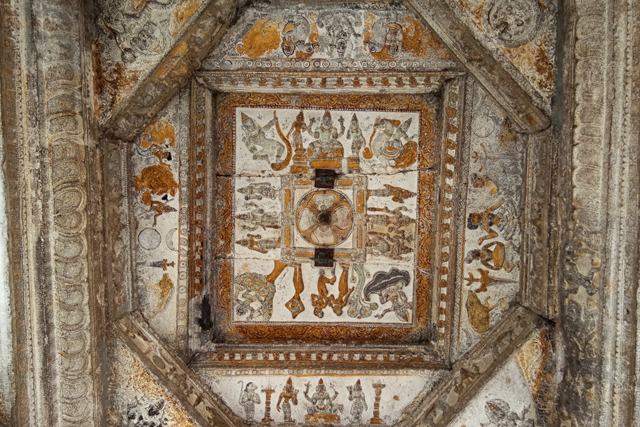



Other common themes include the Vijayanagar crest of the boar and dagger, vidyadhara ridden of palanquins composed of feminine figures of Rati and Manmatha.
![_DSC0106[955]](https://blogvirasatehind.files.wordpress.com/2018/11/dsc0106955.jpg?w=840)
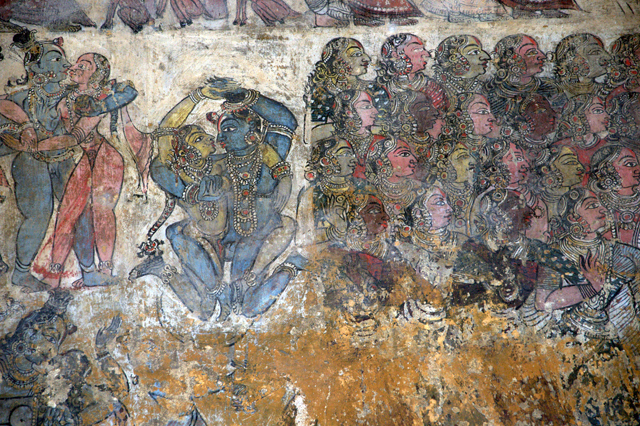




Vijayanagar Murals – Images Courtesy: Vijay Sundararaman Iyer
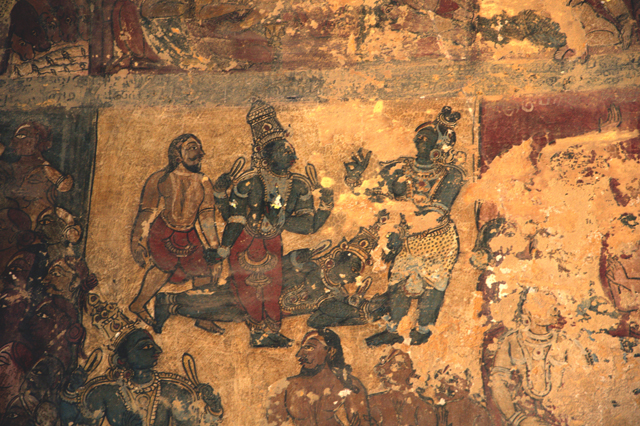
Sadly the Vijayanagar murals are also badly survived. The only prominent colours left are red, yellow, green and black. Yet the leftover outlines depicts prominent figures, strong undulated lines and animated movement.
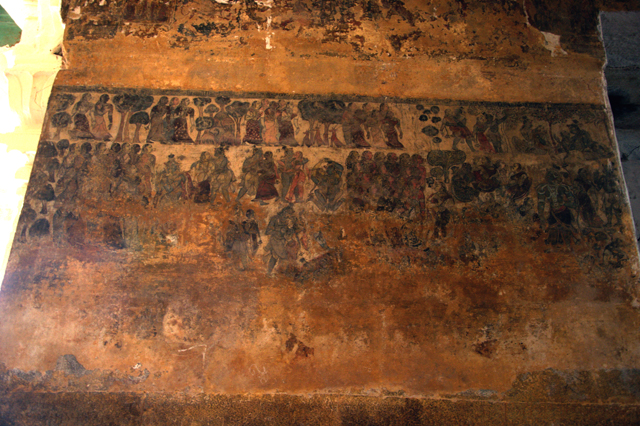
Vijayanagar rulers were succeeded by Nayakas in the 17th century, who had commissioned Jain themes of various bala lilas of Rishabadeva, the first Tirthankara, of Vardaman, of Krishna, of Neminatha and so on. These paintings are illustrated as long elaborate panels in the ceiling of the Jain Temple at Kanchi. The panels are supplemented with the depiction of purnakumbha, flowers along with dancers and musicians.
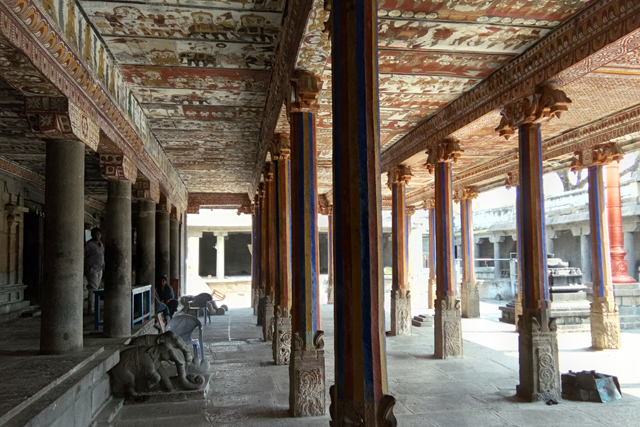
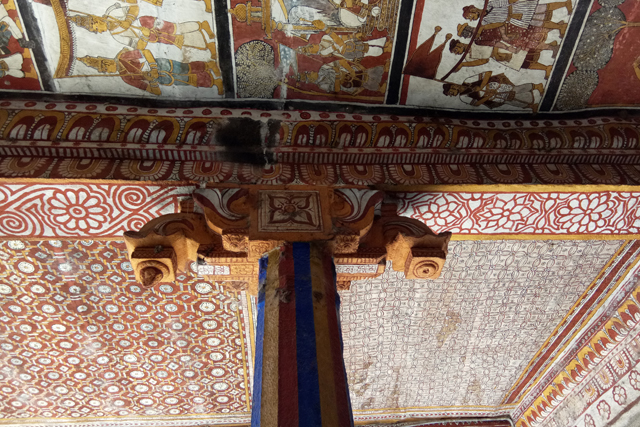
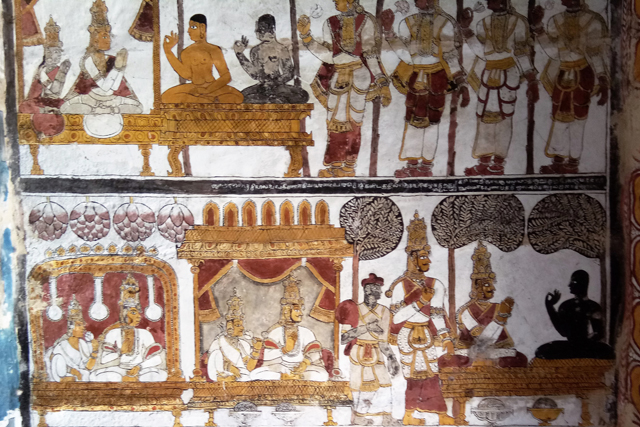
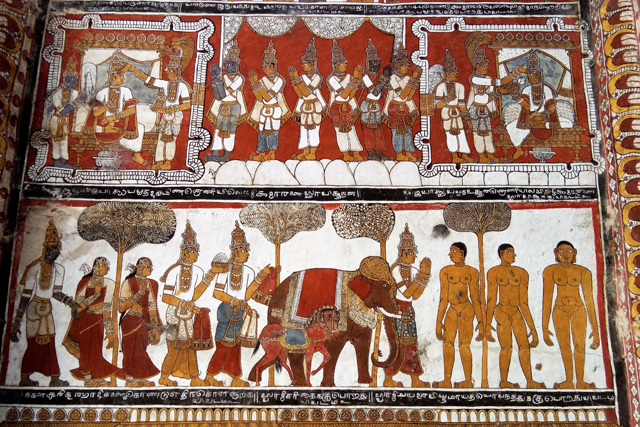
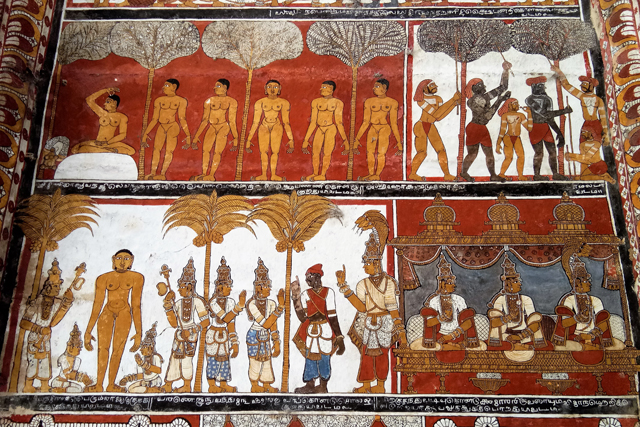











The mural heritage of Kanchi may not be the richest in India but what makes it interesting is the evolution of styles and multiplicity of forms and themes that developed at different periods of history under the patronage of different dynasties. But sadly most of it gone with ravage of time.
Author – Jitu Mishra. He is grateful to archaeologists Vijay Sundararaman Iyer and Aarti Iyer for their knowledge sharing and accompanies at Kanchi in February 2018. Jitu can be contacted at jitumisra@gmail.com
